@the.maska.fam Tried the medicine behind the Capri Sun trick I’ve seen on Tiktok. Didn’t work for this kid. #IntuitTouchdownDance #caprisun #parentsoftiktok #lifehack #fail
♬ original sound – the.maska.fam
Now, picture this: what if the mother was a cunning hacker and the child, an unsuspecting internet user? The juice box is a seemingly harmless email and the concealed medicine as malicious trap set to steal your data. This in essence is what we call phishing, A convincing facade.
The security of our personal and professional information is of paramount importance. One of the most prevalent threats to this security is phishing attacks. Phishing is a form of social engineering attack that aims to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card numbers, and other personal data. This is often achieved by masquerading as a trusted entity such as a bank or a reputable company and duping the victim into opening an email or a text message
What is Phishing?
Phishing scams are designed to trick users into divulging sensitive data, downloading malware, and exposing themselves or their organizations to cybercrime. These attacks are often carried out through fraudulent emails, text messages, phone calls, or websites. The attacker typically masquerades as a person or organization the victim trusts, creating a sense of urgency that drives the victim to act rashly.
Quick Question
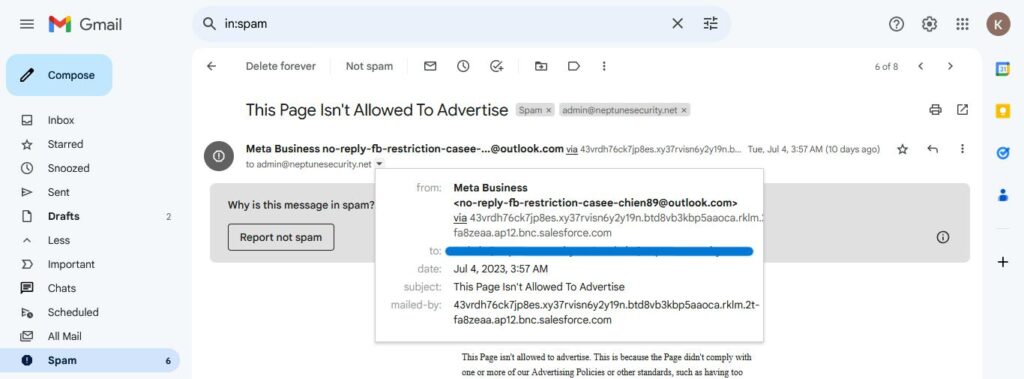
Take a close look at this example of a phishing email we received, claiming to be from Facebook. Can you spot the telltale signs that give it away as a phishing attempt? Keep reading and by the end of this article you’ll be able to confidently identify what makes this email a deceptive phishing attack.
The Impact of Phishing Attacks
The consequences of falling victim to a phishing attack can be severe. For individuals, this could mean unauthorized purchases, identity theft or the stealing of funds. For organizations, a successful phishing attack can lead to severe financial losses, damage to reputation and a loss of consumer trust. According to the FBI, phishing emails are the most popular attack method used by hackers to deliver ransomware to individuals and organizations.
What are the Types of Phishing Attacks?
Phishing attacks can take many forms, each with its own unique tactics and targets. Here are some of the most common types:
Deceptive Phishing
Deceptive phishing is a common scam where fraudsters impersonate legitimate companies to steal personal information or login credentials. In this method, emails are sent in bulk to numerous recipients pretending to be from a trusted organization. These emails contain a link to a fake website that closely resembles the legitimate one. Despite a low success rate, the sheer volume of emails sent ensures that some recipients are tricked into entering their information on the fake site. This captured information is then used by the attacker for malicious purposes such as identity theft or financial fraud. The strategy heavily relies on social engineering and manipulation, hence the term “deceptive.” The effectiveness of deceptive phishing lies not in its sophistication, but in its ability to exploit human error and curiosity.
Spear Phishing
Spear phishing is a targeted form of phishing where attackers focus on specific individuals, organizations, or businesses, rather than sending out mass emails. This method requires substantial preparation, with the attacker researching the victim’s personal and professional details to craft a highly personalized and convincing email. The email, appearing to come from a trusted source, contains a malicious link or attachment that, when clicked or downloaded, can lead to outcomes like malware installation, sensitive information theft, or system control. Due to their personalized nature, spear phishing attacks are often more successful than regular phishing attacks, as they’re more likely to bypass spam filters and gain the victim’s trust.
Whaling
A whaling attack is a type of phishing attack that specifically targets high-ranking individuals within an organization, like CEOs or CFOs. The goal is to steal sensitive company information. These attacks require extensive research from the attacker to create a personalized and convincing message. The term “whaling” refers to the high-value targets, who often have access to a lot of sensitive information. The attacker’s objective is to trick these individuals into revealing information or performing actions that install malware. The consequences of successful whaling attacks can be severe, including significant financial loss, data breaches, and reputational damage.
Vishing
Vishing or voice phishing is a scam where fraudsters use phone calls or VoIP technology to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information or even directly asking for money. They often impersonate legitimate entities or family members, using tactics like caller ID spoofing and automated systems and with the rise of AI technology, these scams have become more sophisticated, enabling more convincing impersonations. The goal is to obtain details like credit card numbers or identity information which can be used for identity theft, unauthorized account access or immediate financial gain. Vishing attacks can be highly effective as they target a wide range of individuals, including those less familiar with email or internet-based scams, and often use urgency or fear to pressure victims into compliance.
Smishing
Smishing or SMS phishing, is a type of phishing attack that uses text messages to deliver a bait message. The victim is usually asked to click a link, call a phone number or contact an email address provided by the attacker. They may then be asked to provide private information such as login credentials for other websites or personal information. The difficulty in identifying illegitimate links can be compounded on mobile devices due to the limited display of URLs in mobile browsers. Smishing can be just as effective as email phishing, as many smartphones have fast internet connectivity.
How to Protect Against Phishing Attacks
Be Vigilant
- Identify Suspicious Requests: Always exercise caution when you receive unsolicited requests for sensitive information.
- Spot Signs of Phishing: Familiarize yourself with common signs of phishing. These can include poor spelling or grammar, requests for immediate action or money, and threats of dire consequences if you don’t comply.
- Avoid Clicking Email Links: Be wary of clicking on links in emails, especially those asking for sensitive information. Cybercriminals often use these links to direct you to fraudulent websites. Instead, open a new browser window and type in the company’s official website address.
- Verify Sender’s Email Address: Always check the sender’s email address. If it’s different from the address you usually receive emails from or if it looks suspicious in any way, proceed with caution. Cybercriminals often use email addresses that look similar to legitimate ones to trick you.
- Beware of “Too Good to Be True” Offers: Remember, if an offer or request seems too good to be true, it probably is. Cybercriminals often use enticing offers to lure victims into their traps. Always verify such offers before engaging with them.
By staying vigilant and understanding the common tactics used in phishing attacks, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to these cyber threats.
Use Two-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring two forms of verification when logging into sensitive applications. This significantly reduces the risk of successful phishing attacks
Firstly, it’s highly recommended to activate the inbuilt 2FA options provided by the websites or applications you use. This is usually a straightforward process that adds a significant layer of protection to your accounts.
However, if you want to take your security a step further, consider these popular 2FA tools:
- Google Authenticator: This is a free security app that can protect your accounts against password theft. It’s easy to set up and can be used with many different websites.
- Authy: Authy offers a more polished user interface compared to Google Authenticator. It also provides a secure cloud backup feature, which can be very useful if you lose your device.
- Microsoft Authenticator: This tool is similar to Google Authenticator but is designed to work particularly well with Microsoft accounts.
For those who prefer physical security keys, consider these options: - YubiKey: Unlike the others, YubiKey is a hardware device that you plug into your computer or connect to your phone. It’s extremely secure and is immune to phishing attacks.
- Titan Security Key: This is a device developed by Google that provides cryptographically secure two-factor authentication.
Remember, the best 2FA method depends on your specific needs and circumstances. Consider your options carefully and choose the one that offers the best balance of convenience and security for you.
Regular Security Awareness Training
Regular Security Awareness Training is vital in preventing phishing attacks. It involves educating your team on identifying phishing attempts, practicing safe link habits, and reporting suspicious activities. As cyber threats evolve, updates to training are necessary. Simulated phishing attacks can provide practical experience, while reinforcing strong password practices and the use of two-factor authentication enhances security. Remember, a well-trained team can be a strong defense against phishing attacks.
Use Security Technologies
Implementing robust security technologies is a crucial step in preventing phishing attacks. These technologies include spam filters, antivirus software, and web filters. Spam filters can detect and quarantine phishing emails, reducing the chance of a user inadvertently clicking on a malicious link. Antivirus software is essential for detecting and removing malware that might be installed on a user’s computer through a phishing attack. Web filters block access to known phishing sites, preventing users from entering their personal information on these sites. Additionally, consider using firewalls for an added layer of protection. For instance, software like Norton 360 provides a comprehensive suite of protections including a spam filter, antivirus, and a smart firewall. Web filtering services, such as Cisco’s Web Security Appliance, can block malicious websites and even scan downloads for potential threats. By using these technologies in conjunction, you can create a robust defense against phishing attacks.
In conclusion, phishing attacks are a serious threat to individuals and organizations, with potentially devastating consequences. It is important to be vigilant and cautious when it comes to emails, text messages, and phone calls that request sensitive information or prompt immediate action. By being aware of the common signs of phishing and verifying the sender’s identity, we can reduce the risk of falling victim to these scams. Implementing two-factor authentication, regularly updating security awareness training, and utilizing security technologies such as spam filters and antivirus software can also provide an additional layer of protection. Ultimately, staying informed and taking proactive measures is essential in safeguarding our personal and professional information from phishing attacks.
Here are a few YouTube videos to help you better understand phishing
For some more security tips checkout our other Posts



